The Future of Generative AI: Trends to Watch in 2026 and Beyond
Home / The Future of Generative AI: Trends to Watch in 2026 and Beyond
Artificial Intelligence
Oct 14, 2025
Generative AI has undergone a metamorphosis, not just as a transformative force with the promise of changing industries, creativity, and human-computer interaction; the year 2026 looks even bigger in terms of advances made possible by physical resources, algorithms, and the demand for personalisation and efficiency. In this blog, we present some emerging trends that will define the future of generative AI and its implications for the years to come.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AIs are artificial intelligence that use a special type of software to create new content: for example, text, images, music, and even complex data structures – all via learning patterns from existing datasets. Simply, in generative AI applications, reality itself is generative – their outputs are new creations instead of the typical application of traditional AI, where input is processed to analyse or classify data. These are powered by models like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and thus large language models like the ones by OpenAI and xAI. As an example, ChatGPT creates human-like text, while tools like DALL-E generate pictures from prompts. At its crux, however, generative AI is imagination – turning things from abstract concepts into things that will be tangible and usable.
Generative AI: Revolutionizing Industries Today and Tomorrow
Healthcare
- Disease Forecasting: AI systems, similar to those developed by AstraZeneca, can detect traits of more than 1,000 diseases even before symptoms appear relying on data from massive health repositories.
- Drug Design: Generative AI is accelerating drug development by mimicking molecular interactions, thus minimizing drug discovery's time and investment.
Future Perspective:
- AI adoption in healthcare could increase personalized medicine, diagnostic accuracy, and streamlining administrative processes, thus enhancing care delivery efficiency.
Manufacturing
Current Impact:
- Product Design & Prototyping: Generative AI is being utilized to develop optimized designs and prototypes, reducing the need for physical prototypes.
- Production Optimization: AI algorithms analyze production data to identify inefficiencies, suggesting changes to increase overall productivity.
Future Outlook:
- The anticipated use of AI is leading toward fully automated production processes where real-time optimization and predictive maintenance practices will become commonplace.
Finance
Current Impact:
- Risk Management: Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems assess financial risk by evaluating large data sets, which allows for increased accuracy of prediction and decision-making.
- Fraud Detection: Generative AI improves the detection of fraudulent behavior by identifying patterns and anomalies in payments data.
Future Outlook:
- The finance sector is headed towards AI-based individualized financial services, with robo-advisory and portfolio management gaining ground.
Education
Current Impact:
- Individualized Learning: AI tools customize education material to an individual's style of learning, increasing student participation and performance.
- Administrative Efficiency: Administrative activities being automated enable teachers to spend more time on teaching and student interaction.
Future Outlook:
- The future of education will witness AI-enabled classrooms, with virtual teachers and AI-powered tests being standard, enabling a more customized learning process.
Entertainment
Current Impact:
- Content Creation: AI creates scripts, music, and visual effects, making the content creation process easier and lowering production costs.
- Audience Engagement: AI scrutinizes the preferences of viewers to suggest customized content, optimizing user experience.
Future Outlook:
- The entertainment sector is set to be revolutionized with AI-created content getting more and more advanced, resulting in new types of storytelling and interactive media.
Top GenAI Trends to Watch in 2026
- Multimodal AI Takes Centre Stage:
One of the most exciting developments happening in the generative AI area is the emergence of multimodal models – those systems that can process and generate seamlessly anything from text to images, audio, and even 3D content. The year 2026 is going to see OpenAI's successors to GPT and the xAI inventions forging ahead into nontextual generation. Just picture AI writing a script, generating the visuals to go with it, and composing a soundtrack, all with one prompt. This merging of modalities surely opens up a lot of possibilities in entertainment, education and marketing. For instance, AI could help filmmakers storyboard entire scenes or help educators design immersive interactive lessons targeting specific individual learning styles. The tough nut? Making sure such models will be mathematically efficient, remaining friendly towards the concerns of smaller organisations.
Also read - Agentic AI vs Generative AI
- Hyper-Personalisation Redefines User Experience:
Generative AI forms the backbone of hyper-personalised experiences. By 2026, enterprises will be deploying AI in the content generation of products and services to meet individual preferences at an unprecedented scale. Imagine e-commerce platforms generating a unique product description and image, or even a virtual try-on experience, for each user. AI tools in healthcare develop personalised treatment plans based on patient data, while procedurally generated worlds in gaming adapt to a player’s style in real-time. This trend depends upon massive datasets and finely tuned models, raising questions about privacy and data security—issues that will need solid resolution as adoption spreads.
- AI Democratisation and Open-Source Momentum:
Generative AI is not merely reserved for tech giants of the future. It has empowered developers, startups, and hobbyists to build their customised models. Open-source frameworks like Hugging Face's Transformers and Meta's LLaMA derivatives are driving future community-inspired innovations wherein tools continue to be more user-friendly and require fewer resources. Expect an increased stake by cloud providers in creating "AI-as-a-service" platform entry barriers considerably lower. Indeed, democratisation cuts both ways. It stirs a spirit of creativity and heightens competition but also increases risks such as abuse (deepfakes). Legislation is likely to develop in tandem to balance these innovations with accountability.
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainable AI:
As generative AI models grow complex, so does their energy footprint. By 2026, sustainability will be one of the top priorities as researchers and industries are running to improve the algorithms and hardware. These model pruning, quantisation, and specialised chip (e.g., TPUs, GPUs)-based techniques don't sacrifice performance for energy savings. Carbon-neutral data centres and renewable energy partnerships have begun to be the norm for AI providers. This isn't altruistic, though – it's purely competitive – pulling in cost savings and public demand for green tech. The future of generative AI will depend on how well power and planet are balanced.
- Creative Collaboration: Humans and AI as Co-Creators:
Generative AI is more than a mere tool; it has transformed into a partner or collaborator. In 2026, more and more artists, writers, and designers will be engaging with AI to expand creative boundaries. Midjourney and DALL-E have metamorphosed into smart assistants that suggest ideas, refine drafts, and occasionally critique works of art. Musicians write songs with "genre-savvy AI", and architects develop structures that were unimaginable a decade ago with generative design. Such use blurs the boundaries between production by human beings and machines and opens up an arena for the arguing of authorship and originality. The key to success? Making it intuitive and responsive to human intent.
Also read - AI for Strategic Planning: Leveraging Data for Long-Term Business Growth
- Real-Time Generative Application:
Speed is everything in 2026, and generative AI is delivering. From instant language translation in video calls to on-the-fly content creation for live events, real-time applications are exploding. In gaming, AI generates dynamic environments as players explore, while in customer service, chatbots craft responses with human-like nuance in milliseconds. This is enabled by edge computing and 5G/6G networks, which push AI to the user and minimise latency, producing a seamless, responsive experience that is highly vulnerable to real-time exploits and requires robust security.
- Ethical AI and Bias Mitigation:
The ethical issues created by generative AI are broadening almost as fast as the technology itself is expanding. In 2026, there was a renewed focus on countering bias, transparency, and building trust. Models are trained on more heterogeneous datasets, and adversarial debiasing is receiving traction with the help of several techniques. Companies are also starting to implement “explainable AI”, a set of frameworks supporting user comprehension of how outputs are generated. Governments and organisations are moving in with guidelines – the United States AI Act 2.0, etc.- pushing for some degree of accountability. The stakes couldn't be higher: these unmitigated biases could worsen the climate for misinformation or also injure marginalised groups. Ethics might be a deciding factor.
- Generative AI in Scientific Discovery:
Beyond creative and commercial uses, generative AI is creating a paradigm shift in science. By 2026, it has accelerated drug discovery through the simulation of molecular interactions, designing materials with desired properties, and even hypothesising experimental designs. xAI is working along those lines for the faster scientific discovery of humankind: AI models are partnered with researchers to address issues like climate change, space exploration, and so on. This trend promises a reduction of the research timeline from years to months; however, proper verification will be required to ascertain the validity of insights generated by artificial intelligence.
Also read - 10 AI and Machine Learning Trends to Watch in 2025
- The Rise of AI Agents:
The age of generative-powered autonomous AI agents will be ushered in by 2026. These agents do not sit idly and respond passively. Imagine AI controlling your calendar, sending your emails, and preparing reports, all without needing a constant watchful eye! For businesses, AI takes care of supply chain logistics, predicts market trends, and even negotiates deals for them. Simply put, this goes one step further from large language models to more decision and task execution capacity. Enter the trouble of having those agents meet human goals and establish boundaries – the hybrid issue of philosophy and engineering.
- MIT FlowER – AI Predicts Chemical Reactions
MIT researchers developed FlowER, an AI which predicts chemical reactions nearly like magic. Envision a GPS for molecules—seeing atoms moving and bonds forming in real-time. This might make it far easier, safer, and less expensive to develop new medicines, electronics, and materials.
- Grok Imagine – AI Creating Movies, Games, and VR
Elon Musk's xAI has launched Grok Imagine 0.9, an AI capable of generating text, images, videos, and even virtual reality experiences. The group aims to develop a completely AI-created movie and video game by 2026. Imagine producing a short film or game without a large crew—AI is making it a reality.
- IBM + Anthropic – AI Agents for Smarter Work
IBM and Anthropic are bringing Claude AI to business software. Businesses can now have AI agents automate work, respond to questions, and assist with decision-making—think of them as virtual colleagues that enable humans to concentrate on strategy and creativity.
- Google Cloud + InVideo – AI Video for Everyone
Google Cloud and InVideo collaborated to enable anyone to convert text into professional-looking videos. No costly software or video editing expertise required—AI handles the heavy work. Small businesses, educators, and artists can now easily and quickly create videos.
- MIT Generative AI Impact Consortium – Robots That Learn Like Babies
MIT's new partnership is training robots to learn the way children do. With the help of "world models," robots are able to observe and interpret the world in order to complete tasks. They can be deployed in factories, houses, or classrooms. The study also has the potential to enhance AI-driven learning tools while eradicating bias.
- Y-Mol – AI That Accelerates Drug Discovery
Y-Mol is a healthcare AI based on LLaMA2 that assists researchers in discovering new medications quicker. It can also forecast the behavior of molecules, identify promising candidates, and examine drug-target interactions—basically providing scientists with an enhanced helper in the lab.
- Delphi-2M – Your AI Health Forecast
Delphi-2M can forecast risks for more than 1,000 diseases from giant population data sets. It's a health forecast for your future—informing doctors and patients how to prepare and make better decisions.
- Edge AI – Smart Decisions Anywhere
Platforms like SiMa.ai’s Modalix run powerful AI models on low-power devices. This means factories, warehouses, or edge devices can make real-time decisions without relying on a massive server farm. Faster, smarter, and more efficient.
- Swarm Robotics + Cloud AI – Robots That Work Together
Researchers are investigating Industry 6.0, in which robots, drones, and autonomous agents work together under cloud AI management. From factory lines to repairs and logistics, these "swarms" can improve work like a perfectly coordinated team, increasing productivity and precision.
- Strategic Fine-Tuning for Regulated Industries
In 2026, companies not just use general AI models anymore—they go for custom models trained with their own data, specific to their industry. This changes how AI is used in important areas like finance, law, insurance and healthcare, where accuracy and rules really matter. Now, many businesses use AI for regulated industries including private LLM tools like Databricks, Amazon Bedrock or OpenAI’s fine-tuning systems to make models that understand their own terms, follow strict regulations and work well with old systems still in place. These more focused AIs give better results and help automate safely in very serious environments. Fine-tuning is not just for tech teams now—it’s becoming a big part of business strategy and growth.
- Voice and Speech Generation
AI speech has come to new levels in 2026 with real-time AI voice synthesis tools, dubbing and interactive audio content. Software such as ElevenLabs, OpenAI Voice Engine and Meta's Voicebox generates human-like speech from just seconds of sample audio and AI voices cannot be differentiated from actual humans. It drives new applications in multilingual dubbing, personalized voice assistants, audio-based narratives and games. Brands are developing personalized voice personas to enrich customer interaction and creators leverage generative speech to generate audiobooks, podcasts and training content instantly. Emotional tone control and real-time generation being features of the past, synthetic voice is soon becoming a central medium of digital interaction.
- Personalised AI Experiences and Hyper-Customisation
Personalisation is at the heart of generative AI in 2026. AI is tailoring content, recommendations and services to individual user preferences in real time. Take for example - personalized AI recommendations for ecommerce. Users receive dynamically generated product pages with specifically designed images and copy. In healthcare, treatment plans are generated based on a patient’s unique genetic and behavioral data. With feedback coming in real time and some clever learning behind the scenes, these models adjust fast — making once-rigid, static content into fluid, context-aware interactions that feel way more alive and in-the-moment.
- Neuro-Symbolic AI Integration
Combining symbolic logic with deep learning, neuro-symbolic AI is gaining traction in fields requiring reasoning and factual accuracy. In 2026, these hybrid systems are revolutionising legal AI, scientific research and education. For instance, legal document generation tools now reason through statutory logic while generating plain-language summaries. This approach mitigates the problem of hallucinations common in pure neural models, leading to more reliable outputs. As a result, neuro-symbolic models are increasingly being adopted in mission-critical domains.
- AI-Powered Digital Personas with Long-Term Memory
In 2026, AI systems aren't just reactive — they recall, adapt and customize over time. Digital personas developed and integrated into apps such as ChatGPT, Claude and Replika can now have long-term memory, allowing for more consistent and helpful user conversations. From recalling a user's preferred writing tone, ongoing projects or health goals, these memory-enabled agents are becoming persistent digital companions. Look for their influence to expand in virtual therapy, learning and executive support.
- Autonomous AI Agents for Business Workflows
AI agents in 2026 are no longer assistants; they are independent actors able to perform multi-step tasks. From reporting and calendar management to automating logistics and supply chain management, these agents become deeply integrated into CRMs, ERPs and productivity suites. They are not like the old bots; they can plan, reason and learn from new data. These new autonomous AI agents doing things on their own are helping companies get way more done — especially in areas like finance, legal stuff, ops and customer service.
- Generative AI for Scientific Discovery
Generative AI is fast becoming a core tool in scientific innovation. In 2026, it is being used to simulate molecules for drug discovery, hypothesise climate models and optimise materials for engineering. Platforms like xAI and DeepMind’s AlphaFold 3 are enabling breakthroughs by significantly reducing research timeframes. Instead of years, new drug compounds are being identified and tested in a matter of months. This acceleration alongwith AI-powered drug discovery tools is redefining the R&D in pharmaceuticals, materials science and space exploration.
- Generative Simulation and Synthetic Data
Training AI models with real-world data often involves privacy risks and scarcity issues. In response, synthetic data generated by AI is becoming mainstream in 2026. It is used in autonomous vehicle testing, finance modeling and healthcare diagnostics. Generative AI simulates edge cases and realistic environments, creating safe and controlled datasets. This enhances accuracy, protects privacy and opens up AI capabilities for industries constrained by data regulations.
- Sustainable and Energy-Efficient AI Models
The increasing sophistication of AI models has rendered energy consumption a vital issue. In 2026, there is model pruning, quantization and utilizing energy-efficient hardware such as TPUs and neuromorphic chips adopted by companies. Cloud providers are investing in data centres driven by renewables, which are carbon neutral. Sustainability is no longer a choice; it's a differentiator for business. Green AI is now a focus area with regulatory incentives for green innovation.
- Open-Source AI and Developer-Led Innovation
Open-source frameworks or tools like Hugging Face, Mistral and Meta’s LLaMA 3 have made it way easier for developers around the world to create and swap their own generative AI models. In 2026, open-source is not just alive — it’s booming. It’s breaking down the hard things, letting more people join in and push things forward. Developers are building all kinds of apps, from niche image tools to custom chatbots, using smaller, tuned-up models. The whole space runs on sharing, testing stuff out and moving fast across different areas.
- Creative Collaboration: AI as a Co-Creator
Creatives in 2026 are no longer isolated. Platforms such as Midjourney, DALL·E and Suno are making AI a full-fledged co-creator. AI is used by writers for ideation, musicians create songs using genre-specific prompts and designers construct prototypes quicker than ever before. The creative process is now complemented with AI feedback cycles and dynamic style adjustment. The trend is revolutionizing the roles played by artists and is fueling arguments on authorship, originality and ownership.
- Generative AI in Real-Time Applications
Speed is a characteristic in 2026. Generative AI drives live applications like real-time language translation, instant video content generation and interactive gaming worlds. Latency is significantly minimized with the help of edge computing and 6G connectivity. All this allows for smooth, dynamic experiences across entertainment, customer service and learning. Businesses are building AI that not only reacts but predicts needs in the moment.
- AI-Generated Code and Autonomous Development
Coding is evolving from a manual task to a co-piloted or even autonomous process. Generative tools like GitHub Copilot X, Amazon CodeWhisperer and GPT-Engineer are creating entire applications from simple prompts. Developers are now validators and prompt engineers rather than line-by-line coders. In 2026, full-stack prototypes can be spun up in minutes, with AI managing UI design, backend logic and API integration. This shift is revolutionising how software is conceived and delivered.
- Secure and Watermarked Generative Content
Trust in AI-generated content is critical. In 2026, embedded watermarking and content provenance are becoming standard features. Technologies from companies like Adobe and Microsoft ensure that AI-generated images and text can be traced and verified. These tools are helping curb misinformation, support copyright compliance and maintain brand integrity. Watermarked generative content is now a requirement in journalism, digital marketing and legal domains.
- Generative AI in Robotics and Embodied Systems
Robotics is being redefined by generative AI. In 2026, robots are not just programmed but dynamically trained via language and vision-based AI models. Embodied systems like Tesla Optimus and Boston Dynamics robots can now learn tasks on the fly from verbal or visual prompts. This is revolutionising manufacturing, eldercare, home automation and logistics. The fusion of LLMs and robotics enables adaptive, human-aware interactions.
- AI-Native Interfaces and Ambient Computing
The interface revolution is underway. In 2026, AI-native interfaces are moving beyond screens to voice, gesture and environmental cues. Devices like Humane AI Pin and Apple’s generative voice assistants are ushering in ambient computing. Users interact with AI through natural, context-driven conversations. These interfaces learn over time and proactively support users, making traditional UI elements obsolete. This is the foundation of seamless human-AI interaction across smart homes, wearables and workplaces.
- AI-Powered Video Generation & World Simulation
In 2026, text-to-video models like OpenAI’s Sora and Google DeepMind’s Veo 3 are revolutionizing the creative industry. Sora, now integrated into ChatGPT Pro, can generate coherent, multi-frame clips and even extend existing videos—a breakthrough in narrative storytelling. Veo 3 introduces synchronized audio—speech, ambient sounds, music—making AI-generated video a fully immersive media format. Tools and AI-generated video content platforms like Runway, Ray2, Kling 2.0 and Pika Labs underscore a broader AI-video arms race involving major industry players.
- Neuro‑Symbolic Generative Diffusion Models
Moving beyond hybrid reasoning, 2026 introduces Neuro‑Symbolic Diffusion (NSD)—a powerful blend of deep generative capabilities and symbolic logic. This interleaving ensures that outputs conform to physical laws or regulatory rules. NSD offers provable consistency for use cases like molecular design, physics simulations and trajectory planning—where safety and reliability are non-negotiable. It sets a new benchmark for scientific and engineering applications.
- Efficient Video Model Training & Open Sora 2.0
Cost-effective innovation continues with Open Sora 2.0, an open-source, commercial-grade video model trained on just US $200,000. It rivals proprietary models like Runway’s Gen‑3 in quality and performance. This breakthrough democratizes advanced video generation, enabling startups and researchers to access cutting-edge tools without massive budgets. It marks a turning point for accessible, scalable video AI.
Economic Potential of Generative AI
Generative AI is not merely a technological sensation but could also become an economic powerhouse. McKinsey estimates that Generative AI’s economic impact could fall between $2.6 trillion and $4.4 trillion per year globally, which is more than the entire GDP of the UK in 2021 ($ 3.1 trillion). This would be a shift of 15–40% in the total value AI could provide across industries.
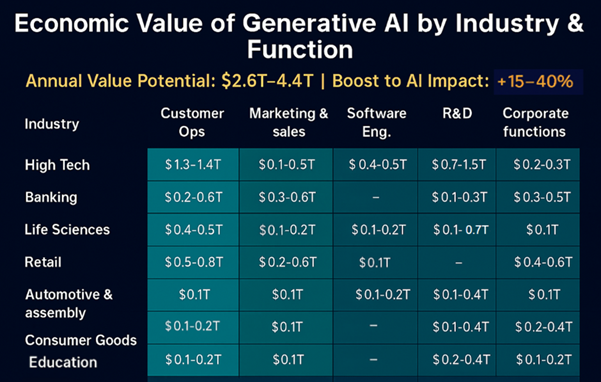
This is due in part to GenAI’s ability to drive productivity in many different areas including:
- Customer operations
- Marketing and sales
- Software engineering
- Product development
- Back office support
Ethical Issues with Generative AI
Generative AI is emerging as a potent engine of change, the applications of which are disrupting sectors from entertainment to health care. But such astonishing developments also bring challenges of an ethical kind. Deepfake technologies and ubiquitous synthetic media have introduced ambiguity regarding the meaning of reality in an age where misinformation threatens the very notion of public trust. In creative industries, especially in areas such as music and art, the ability of generative AI to copy a specific human style has raised issues of authorship, copyright, and the worth of an original work.
In addition to creativity, many of the inner workings of AI models are not transparent; thus understanding how decisions are made is challenging. Bias in training data tends to amplify unfair outcomes further! This would have implications for accountability and trust. The future will be developing transparent, explainable, and ethical AI systems that create responsible innovation while preserving human creativity and integrity.
Conclusion
Expectations for generative AI's future may be heavily underlaid with promise and complexities. Creative ecosystems may be fully autonomous by 2030, or we might see quantum-enhanced generative models or artificial intelligence that better mimics human reasoning. With great power comes great responsibility. The trends of 2026 will include multimodality, personalisation, sustainability, and ethics. It will be important to collaborate between technologists, policymakers and society as we venture forward with this technology, now that we are realising there are benefits we want to make use of, as well as that we need to take care of the risks involved. There is one certainty: it is not just paving the future; it is redefining what is possible.
FAQs:
- What is Generative AI in simple terms?
Generative AI is a form of artificial intelligence that can "create" such as text, images, video, or music — it creates unique content based on what it understands from existing data instead of just providing answers.
- How does Generative AI actually work?
GenAI is trained to recognize patterns from vast amounts of data and predict what happens next — in the case of text, the next word, in the case of video, the next sound, and the next image in the case of images. This is why ChatGPT or image creators can generate content that appears incredibly real, and quickly.
- What are some real-world examples of Generative AI?
You have Generative AI right in your hands and everywhere! ChatGPT for text, DALL·E and Midjourney for images, and Synthesia for video, and even Soundful for music — Generative AI is disrupting every segment of the industry.
- Is ChatGPT an example of Generative AI?
Yes, without a doubt! ChatGPT is perhaps the best-known example of Generative AI. It generates natural, human-like text from what you enter — that is, good for writing emails, essays, ideas, and assisting with code.
- How do people use Generative AI in their daily lives?
People use GenAI to generate messages, create logos, generate photos, summarize notes, or even plan meals. It is increasingly becoming a silent intelligent assistant at work within professional settings, in learning, and in innovation in everyday life.
- What are the advantages of employing Generative AI?
It will save time, lead to greater creativity, and allow anyone to produce content at levels approaching professional work much faster. Whether it is for writing or for businesses, GenAI is a tool that simplifies complicated tasks and makes life easier.
- What are the dangers or the drawbacks of Generative AI?
It has the potential to generate incorrect or biased data, and deepfakes can be abused. That is why it is so critical that the AI is used responsibly and transparently.
- How is Generative AI unlike regular AI?
Normal AI analyzes and forecasts — say, suggesting a movie. Generative AI generates — it develops a story, creates music, or designs an image. It's creative, not analytical.
- Can Generative AI generate images, videos, or music?
Yes! GenAI tools can create pictures, song music, 3D designs, or even movie footage. It's transforming digital art and entertainment creation.
- Will there be human replacement by Generative AI in the future?
Not at all. It will do the repetitive stuff but generate new jobs — in AI ethics, design, and data science. The future is for people who learn to collaborate with AI, not compete against it.
Latest Updates & Articles
Stay Connected !! To check out what is happening at EIMT read our latest blogs and articles.







