Key Management Theories: Classical and Modern Approaches to Organizational Effectiveness
Home / Key Management Theories: Classical and Modern Approaches to Organizational Effectiveness
MANAGEMENT
Feb 26, 2026
Imagine a company with inefficient operations, disengaged employees, and declining productivity. On the other hand, company B, where employees are motivated and performing at their peak potential. What’s the difference? The answer boils down to effective management.
In simple terms, management theories are defined as how organizational structure works to increase effectiveness. It helps organizations to focus, communicate, and evolve. Management theories also allow leaders to focus on the core aspects of the organization.
In this blog, we dive deep into the theories and how they can be applied to enhance organizational effectiveness.
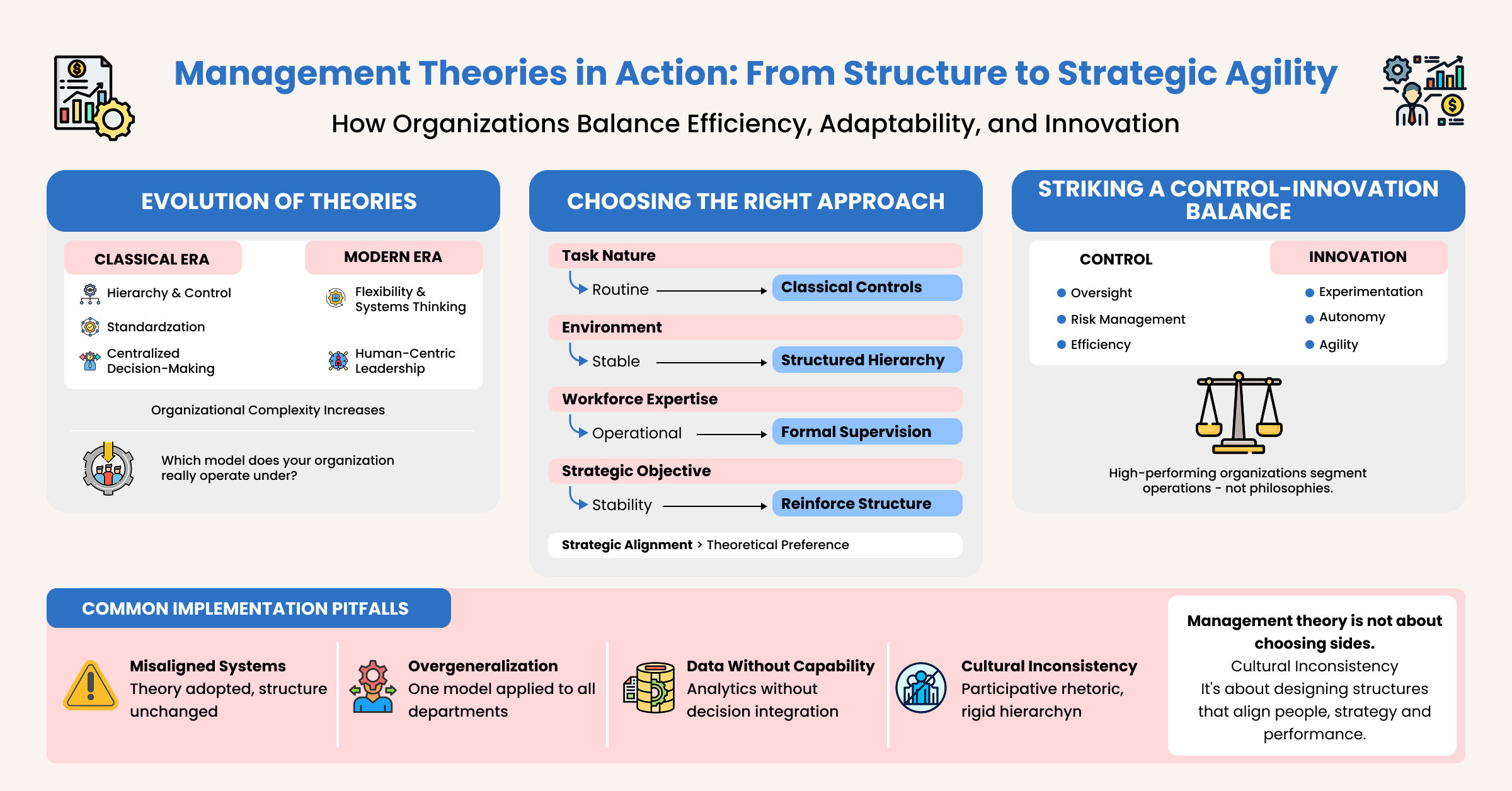
Management Theories: Evolving from Efficiency to Adaptability
Management theories developed alongside changes in industrial organization, patterns of employment, and operating conditions within enterprises. Early approaches were basically about how to arrange the work, keep many employees working together, and still have control over the production. However, when organizations became larger and more diverse, it was clear that just formal structures and rules were not enough to explain the performance of organizations. Attention gradually extended to the role of human behavior, social relationships, and the external environment in shaping managerial outcomes.
An understanding of this development is important for managers working in contemporary organizations. Management theories are not applied as fixed or exclusive models but are used selectively to address specific organizational requirements. Each approach contributes to how managerial authority is exercised, how activities are coordinated, and how organizations respond to stable as well as changing conditions.
Classical Management Theories
Classical management theories are based on the worker's efficiency. It is designed to fulfill the worker's only physical and economic needs. This theory advocates a specialization of labor, centralized leadership, and profit maximization.
Scientific Management Theory (Taylorism)
Taylor's scientific management theory is focused on efficiency. As per the Taylor mindset, employers should appreciate workers for the increased product rather than scold them for every minor mistake. This theory is based on 4 core principles.
- Each part of a work has a science to it.
- Employers should hire, train, and cultivate employees using a scientific approach.
- There should be a healthy collaboration between employees and employers.
- Employers should divide work and responsibilities among employees.
Taylor's application of time-and-motion studies at Midvale Steel and Bethlehem Steel raised productivity by leaps and bounds—e.g., pig iron loading output increased from ~12 to ~47 tons/day, with employees making ~60% more in pay.
His “one best way” principles remain foundational: Gantt charts, performance measurements and process flow analysis are used extensively today.
Implementation of Taylor’s Management Theory
Here are some tips for the successful implementation of this theory:
Break Down the Tasks into Subtasks: Managers or employers who follow Taylor's theory break the entire project into tasks and assign them accordingly. This makes the entire process more organized and efficient.
Delegation and Training Workers: According to Taylor, employers should find the most efficient way to complete the given tasks and then delegate them as per the employee's skills and abilities. Management should train those workers in whatever method was identified to complete the assignment more efficiently.
Measure Performance: Managers should track the performance to ensure efficiency for your business and your workforce. This helps to achieve Taylor’s goal of maximum prosperity.
Bureaucracy Theory (Max Weber)
Max Weber's Bureaucracy Theory is one of the most efficient classical theories. It is designed for private businesses and public offices. According to this theory, everyone is treated equally, and work responsibilities are divided by each team’s area of expertise. This theory is based on the 6 major principles.
- Formal hierarchical structure
- Rule-Based Management
- Functional Specialty Organization
- Up-focused or in-focused mission
- Impersonal Communication
- Employment Based on Technical Qualification
Implementation of Weber’s Theory in Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
Here are a few tips that you should consider.
Stress Relief and Fairness: This theory gives employees peace of mind and fairness in business. This can be helpful to boost morale. For example, clearly defined rules for your company (employee handbook) can help protect the business and its employees.
Use SOPs: Consideration of standard operating procedures enhances the efficiency of the employees. For example, in the manufacturing business, having a set of rules in place, such as how equipment should be operated, can reduce workplace injuries.
Neo Classical and Humanistic Perspectives
The emphasis of classical management theories on formal organization and output efficiency revealed certain practical limitations, particularly in addressing human behavior at work. In response, neo-classical and human-oriented approaches developed to account for factors beyond prescribed roles and procedures. These approaches drew attention to behavioral aspects of management, highlighting the influence of social interaction, individual attitudes, and workplace conditions on employee performance.
According to the neo-classical theory, organizations are seen as a context in which informal associations, leadership behavior, and communication patterns are of prime importance in determining the outcomes. In this regard, work effectiveness is seen to be affected by the employees' perception of recognition, involvement, and psychological well-being. As a result, the managerial attention is not confined to task allocation but also encompasses cooperation, group cohesion, and decision-making.
This development represented a significant change in managerial thinking. Management began to be understood not only as an administrative activity but also as a process involving social coordination and interpersonal capability. While organizational structure and authority remain relevant, neo-classical theory maintains that attention to human behavior is essential for achieving consistent and long-term organizational performance.
Modern Management Theories
Modern management theories were made in the mid-20th century. It is built upon the foundations of the classical theories. They provide a holistic understanding of organizations and management practices. This theory breaks down the complexities of human behavior and the dynamics of the business environment.
Human Relation Theory
Human relations theory is based on the belief that people want to be part of a team that focuses on development and growth. Therefore, if employees get special attention and are encouraged to participate, they are motivated to do productive work, which leads to high-quality work.
Human Relation Skills
There are 3 core human relations skills that you should have to consider
- Communication is an essential skill to practice human relations. Effective communication ensures employees are on the same page as well as feel motivated and valued at work. The mode of communication should be anything verbal or written.
- Conflict Skills. As a manager, you have to deal with the different personality types, worldviews, and goals that make universal agreement difficult. Therefore you must be comfortable and well versed in conflict resolution.
- Multitasking: Managers face lots of issues and questions to solve daily. They are accountable for themselves as well as the success of their team. A good leader has the skill to manage multiple tasks at once. It can be through prioritization,
Implementation of this theory in SMB is easy. As a manager, you can easily develop these skills and implement human relations management practices in your organization.
Systems Approach Theory
It is commonly considered the foundation of organizational development. In this approach, we look at organizations as systems and sub-systems that interact with one another to create an overall organizational system. In the system approach, employees are more focused on achieving a collective goal for an organization rather than operational output.
Example: Most organizations are using enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to consolidate departments such as operations, HR and finance. This cross-functional integration is an example of the systems approach, where everything within a business functions as a cohesive entity.
Contingency (Situational) Theory
Contingency theory states that there is no one best method for managing an organization. The effectiveness of management and leadership practices varies with several situational factors like company size, team structure, external environment and nature of the task in question. Instead of adhering to set principles, this method encourages flexibility in molding strategies as per individual circumstances. The theory is based on Fiedler's study, which indicated that leadership effectiveness increases when style and situation match.
- In 2022, an empirical study revealed that 209 leaders of various organizations affirmed that aligning leadership behaviors with situational demands greatly enhanced team performance as well as organizational control.
- Meta-analyses indicate that the use of this method is consistent across industries and nations, though with varying effectiveness when the organization’s size and outside forces are involved.
Core Principles of Contingency Theory:
- The style of management has to be flexible to the prevailing environment.
- There is no one best way to lead or decide.
- Success in leadership is a matter of fitting the manager's style to the requirements of the situation.
- Success for the organization is derived from aligning the right strategy with the right setting.
Implementation of Contingency Theory
Below are some advice on applying this theory successfully in practice:
- Monitor the Environment Regularly: Managers should continuously measure internal and external elements, such as employee preparedness, market needs and resources available.
- Adjust Leadership Style: Instead of using a consistent style, leaders should adjust between directive, promotive, collaborative or delegating styles depending on maturity level of the team and the complexity of the task.
- Customize Solutions: Focus on solutions that fit your organization’s unique situation—avoid generic options that overlook your specific context.
Quantitative/Management Science Approach
The quantitative method is centered on the utilization of mathematical and statistical techniques in making decisions. It is concerned with data-driven solutions, modeling, and optimization methods for addressing intricate business problems. The quantitative method is widely applied across logistics, operations, finance, and supply chain management.
- A Moroccan examination of 190 industrial companies discovered that the tailoring of management control systems according to contingency variables (i.e. firm size, technology) resulted in quantifiable improvements in organizational effectiveness and decision-making accuracy.
- Wider research establishes that data-driven models improve resource allocation and strategic planning in industries such as logistics and finance.
Principles Behind Quantitative Approach:
- Business decisions should be made on objective facts and quantifiable results.
- Models and simulations aid in predicting results and enhancing decision quality.
- Efficiency can be optimized using optimization methods.
- Quantitative tools enhance improved resource allocation and performance measurement.
Implementation of the Quantitative Approach
Following are methods to put this theory into practice effectively:
-
Use Decision-Making Models: Use tools such as linear programming, forecasting, or simulation to experiment with strategies prior to implementation.
-
Leverage Data Analytics: Incorporate business intelligence tools for tracking KPIs and extracting actionable insights from large data sets.
-
Promote Evidence-Based Management: Prompt managers to support decisions with facts avoiding reliance on instinct in areas like financial planning and staff assessments.
Holacracy
Holacracy theory, brought forward in the 2000s by Brian Robertson, is a distributed management framework that shares power between self-organizing teams instead of keeping hierarchical top-down structures. It inspires employees to play multiple roles and work with greater independence, enabling flexibility, creativity, and accountability.
- A 2024 meta-analysis of firms applying Holocracy found advantages like increased innovation and transparency—particularly in small to medium-sized businesses—but found effectiveness was influenced by leadership flexibility and cultural alignment.
- Notable implementers are Zappos and Medium. Zappos experienced a 14-18% self-imposed attrition rate in the transition, demonstrating both promise and pitfalls
Core Principles of Holacracy:
- Jobs are described in terms of work, not individuals.
- Decision-making is allocated to roles, not titles.
- Authority is conveyed through ordered governance.
- Transparency and accountability are intrinsic.
Implementation of Holacracy
Advice for rolling out Holacracy in your organization:
- Define Clear Roles: Assign roles by function, not by position. Roles can shift based on shifting business requirements.
- Hold Governance Meetings: Have regular team meetings to evolve roles and rules, so that the organization changes organically.
- Encourage Self-Management: Let employees take initiative, make decisions within their roles, and own results.
Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
Emotional intelligence (EI) leadership is the capacity to comprehend, know, and manage one's own emotions and those of others. Individuals high in EI are superior at creating trust, minimizing conflict, and enhancing performance in people-focused organizations. Made popular by Daniel Goleman during the 1990s and perfected with the aid of neuroscience during the 2000s. Large companies like Google and Deloitte have embedded emotional intelligence in their leadership programs. High EQ leaders have been known to create improved team morale, reduced turnover and enhanced interpersonal relationships within teams.
- A 2018 survey of 217 software developers discovered that highly psychologically safe teams—strongly correlated with emotionally intelligent leadership—had 30–71% greater job satisfaction and performance.
- According to a 2023 McKinsey report, organizations led by managers with high emotional intelligence were 25% more likely to retain top talent.
- Many workplace researches establish that emotionally intelligent managers decrease turnover and enhance team cohesion.
Key Principles of Emotional Intelligence:
- Good leadership has self-awareness as its basis.
- Empathy creates more effective relationships and groups.
- Self-regulation facilitates level-headed and clear decision-making.
- Social skills improve influencing and communication.
Implementation of Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
Here is how to integrate emotional intelligence into everyday management:
- Build Self-Awareness: Ask leaders to identify their emotional triggers and communication patterns through journaling or mentoring.
- Emphasize Empathetic Listening: Teach managers to listen actively and hear employee views, particularly in cases of feedback or conflict resolution.
- Develop a Supportive Culture: Encourage an open communication atmosphere, emotional intelligence, and inclusive leadership.
Modern Management Theories: Complexity and Context
Modern management theories emerged as organizations began operating across national boundaries, adopting new technologies, and facing less predictable operating conditions. Earlier managerial approaches offered limited guidance in such circumstances, prompting the development of theories that account for variation in organizational settings. These newer approaches recognize that managerial decisions are shaped by external conditions as well as internal organizational arrangements.
In contrast to traditional approaches, modern management theories do not presume that a particular approach to management can lead to effective outcomes in all circumstances. Organizational performance is perceived to be influenced by certain factors, such as the type of industry, size of the organization, employees, and the level of uncertainty in the external environment. Therefore, managers are expected to evaluate the circumstances before identifying the structures and processes to be adopted.
There are several modern approaches that view the organization as a set of interrelated activities, rather than as a collection of separate functional units. Decisions in one function, such as personnel or production, may have an impact on other functions. By recognizing these interrelationships, managers can better coordinate activities and eliminate inefficiencies.
Modern management theories place greater emphasis on using analysis to justify managerial decisions. Techniques like performance analysis, planning sessions, and review meetings help managers to evaluate alternatives and forecast future needs. This enables organizations to keep a sense of direction while modifying their practices according to changing situations.
Applications of the Management Theories to Enhance Organizational Effectiveness
Improving Decision Making
With the help of scientific management, we can understand deeply the work processes and identify inefficiencies. This helps organizations to make more informed decisions. For instance, analyzing employee productivity data can help determine the optimal staffing levels or identify areas for process improvement.
Boosts Employee Morale
The application of human relation theory helps to create a positive work environment and increase employee recognition, which can significantly boost employee motivation. It also provides the opportunity for social interaction, regular feedback, and appreciation.
Enhancing Organizational Flexibility
The application of bureaucratic structures can provide stability and order. It helps to introduce more flexible roles and encourages employees to experiment and innovate.
Classical vs Modern Management Theories: Comparative Overview
| Dimension | Classical Management Theories | Modern Management Theories |
| Core Focus | Operational efficiency, task specialization, and structural control | Adaptability, organizational effectiveness, and strategic alignment |
| View of organization | A mechanistic system with clearly defined roles and authority | A dynamic system of interdependent units influenced by environment |
| Decision-Making | Centralized and top-down approach is followed | Decentralized and context-driven |
| Management Style | Directive and supervisory | Participative and facilitative |
| Employee Perspective | Workers viewed primarily as resources for production | Employees seen as strategic contributors and knowledge assets |
| Motivational Bias | Financial incentives and compliance | Psychological, social, and developmental factors |
| Flexibility | There is limited flexibility; reliance on fixed rules and procedures | Flexibility is high; responsive to change and uncertainty |
| Environmental Sensitivity | Assumes stable and predictable conditions | Designed for volatile and complex environments |
| Role of Leadership | Emphasis is on authority and control | Emphasis is on influence, coordination, and empowerment |
| Use of Data and Analysis | There is minimal reliance on analytical tools | Strong focus on data, models, and performance metrics |
| Suitability | Best for routine operations and standardized processes | Best for innovation-driven and knowledge-based organizations |
| Long-Term Orientation | Efficiency-focused, short-to-medium-term outcomes | Sustainability, learning, and long-term resilience |
Selecting the Right Management Approach: A Strategic Framework
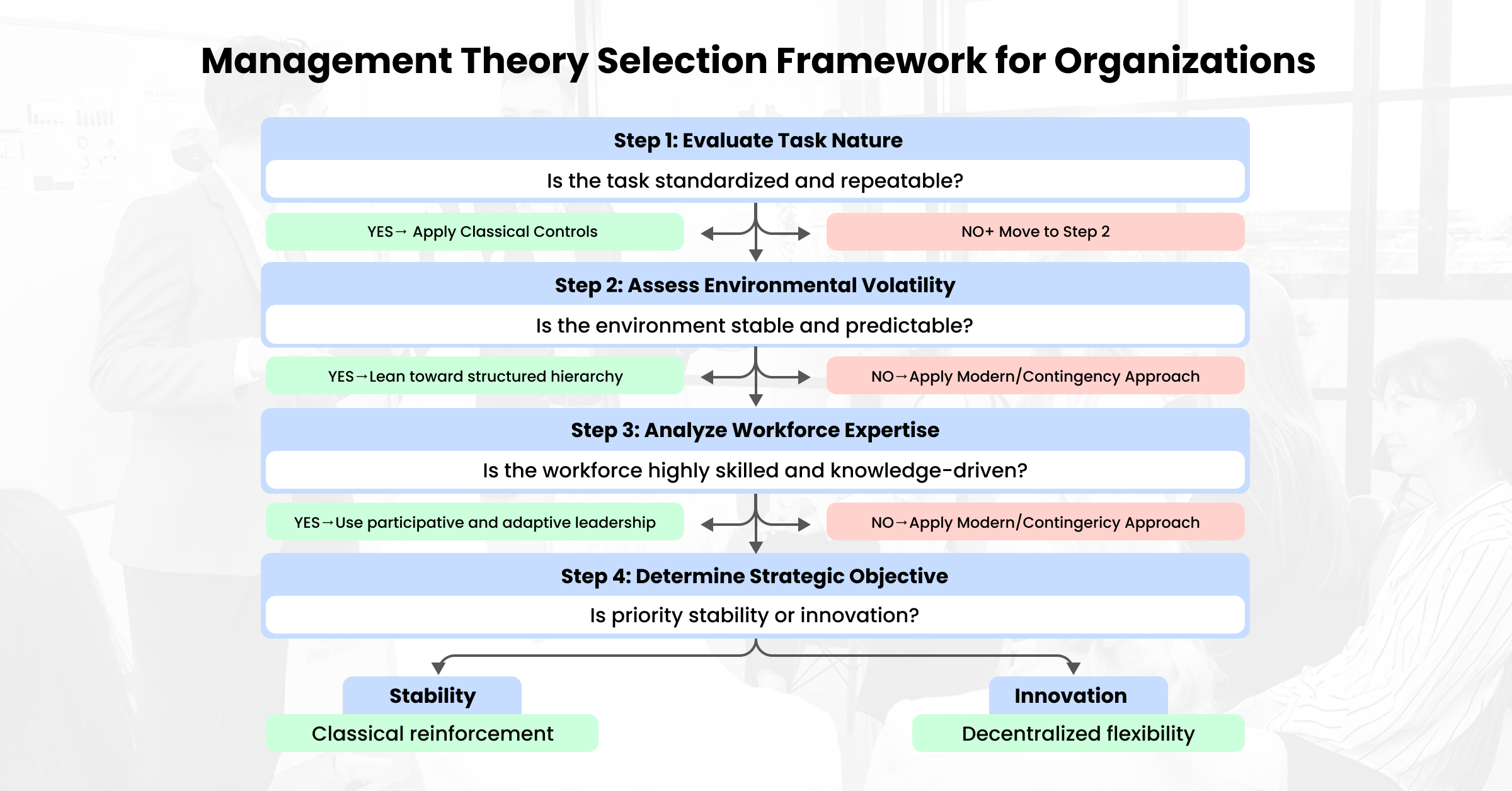
Although classical and modern management theories offer different viewpoints, the key to effective management lies in choosing the appropriate management style for the given situation. Instead of treating these theories as rival approaches, managers need to use them diagnostically based on structural and environmental factors.
- Task Complexity and Standardization
Routine and standardized tasks, such as manufacturing, financial reporting, or regulatory work, are well-suited to classical approaches that stress hierarchy, procedure, and output. In contrast, complex, ambiguous, or innovation-oriented tasks demand participative and flexible approaches that correspond to modern theories.
- Environment Volatility
Organizations in stable and predictable environments can maintain efficiency through formalized authority structures. In contrast, organizations in environments characterized by technological turbulence, global competition, or environmental shifts demand contigency-based flexibility.
- Composition of Workforce
When workforces are mainly composed of operational employees, formal supervision helps to increase accountability. In knowledge-intensive places where workforces are composed of highly competent professionals, autonomy, teamwork, and internal motivation are the major drivers of performance.
- Organizational Lifecycle Stage
Startups may need flexible experimentation, while growing organizations need to impose structure to prevent organizational fragmentation. Mature organizations usually implement hybrid models that seek to balance stability with flexibility.
This framework views management theory as a decision-making tool rather than an ideology.
The Control-Innovation Balance in Modern Organizations
One of the issues that keep arising in organizational design is how to achieve a balance between control and innovation. As organizations grow in size, there is a greater need for control, accountability, and monitoring of performance. But innovation, which is critical for sustained competitiveness, flourishes in an environment that encourages experimentation, adaptability, and decentralized decision-making.
Too much emphasis on control can lead to bureaucratic rigidity, which can slow down response and discourage initiative. Conversely, too much decentralization can undermine coordination and accountability. This dilemma is overcome by high-performing organizations through structural segmentation.
Core operational divisions, for instance, finance, compliance, and supply chain, are governed by classical principles in a structured manner to ensure reliability and risk management. At the same time, innovation-driven decisions, for example, research and development, product development, and strategy, are governed by adaptive and participative principles in accordance with modern management theories.
The dual-operating system model helps organizations ensure execution discipline while maintaining strategic agility. Strategic success is achieved not through theoretical consistency but through strategic alignment between control and innovation.
Common Implementation Pitfalls in Applying Management Theories
Effective management theories will only produce positive outcomes if they are fully integrated into organizational structures, systems, and leadership practices.
- Management theories will only be successful if they are implemented in a manner that is consistent with the organizational systems and leadership behavior, and not just rhetoric.
- Participative leadership style with rigid hierarchical structures confuses people and leads to a lack of trust.
- Without the right analytical skills and decision integration, data-driven strategies will not work.
- Using the same theory for all departments is inefficient because of the differences in functions.
- For effective implementation, there should be structural consistency in terms of performance measures, organizational structures, and reward systems that support the chosen leadership style.
Final Thoughts
This blog highlights the evolving nature of management theories and how they help to enhance organizational effectiveness. Effective management requires a holistic approach. It embraces continuous learning, adapting new technologies, and prioritizing employee well-being. Organizations can easily navigate the challenges of the modern business landscape and achieve sustainable success.
FAQs
1. What are the differences between classical management theories and modern management theories?
Classical management theories mainly focus on hierarchy, standardization, and efficiency. On the other hand, modern management theories emphasize flexibility, human behavior, environmental complexity, and data-driven decision-making.
2. Why are management theories important in the today's world?
Management theories are significant because they provide structured frameworks that assist leaders in diagnosing organizational problems, designing efficient systems, and making decisions based on facts.
3. How do modern management theories make organizations flexible to change?
Modern management theories provide decision makers with analytical and systemic thinking skills as well as the learning from past experiences, thus enabling changes in strategies and structures for adaptation to organizational change.
4. Can multiple management theories be used together?
Yes. Hybrid management practices are a combination of the best features of classical, humanistic, and modern management theories that help meet the various needs of organizations.
5. Which management theory is best suited for dynamic business environments?
Contingency and systems management theories focus on alignment and interdependence respectively, and thus, they are suitable for dynamic business environments.
Latest Updates & Articles
Stay Connected !! To check out what is happening at EIMT read our latest blogs and articles.







